What is Solar Power and How Does It Work?
Solar power is rapidly gaining attention as a renewable energy source. It harnesses sunlight to generate electricity, which can power homes and businesses. This innovative technology offers many benefits. It reduces reliance on fossil fuels and lowers carbon emissions. Solar energy is clean and abundant.
Understanding how solar power works is vital for its broader adoption. Solar panels, made up of photovoltaic cells, convert sunlight into electricity. This process involves absorbing sunlight and generating direct current (DC) electricity. An inverter then converts this to alternating current (AC), making it suitable for home use.
However, not everything is perfect. Solar power relies on sunlight, so its efficiency varies with weather and location. Additionally, the initial cost of installation can be high for many. Despite its challenges, solar power presents a promising path towards a sustainable future. Its continued innovation and development are essential to overcoming these obstacles.

What is Solar Power? A Comprehensive Overview of Solar Energy
Solar power harnesses the sun's energy to generate electricity. It is increasingly popular due to its renewable nature and potential for sustainability. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar energy accounted for nearly 10% of the global electricity generation in 2020. This percentage continues to grow as technology advances and costs decrease.
Solar panels convert sunlight into electricity through photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells generate a flow of electricity when exposed to sunlight. The energy produced can be used immediately or stored for later use. In 2022, the average cost of solar panels dropped by 25%, making it more accessible for households and businesses alike. However, there are challenges to consider. The efficiency of solar panels can be variable based on location and weather conditions. Maintenance and the environmental impact of manufacturing solar panels are also concerns.
Nevertheless, solar power presents a clear opportunity for reducing reliance on fossil fuels. In some regions, it has become a critical part of energy strategies. Despite significant progress, it is essential to reflect on the limitations and the need for further advancements in storage technology. This balance between benefits and drawbacks shapes the current landscape of solar energy.
Solar Energy Production by Source (2022)
The Science Behind Solar Energy: How Photovoltaic Cells Work
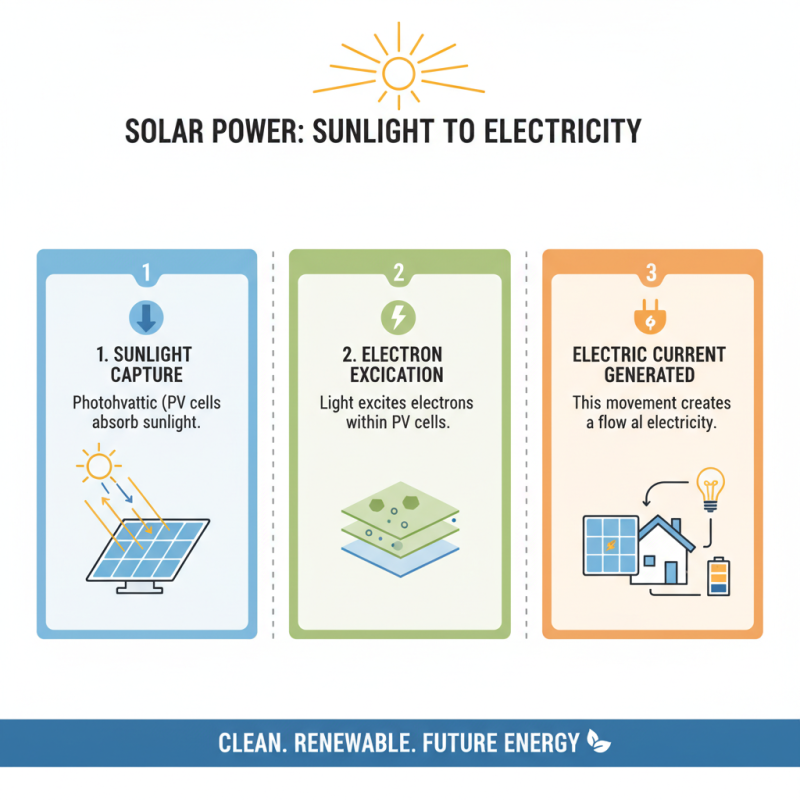
Solar power harnesses sunlight to produce energy, utilizing photovoltaic (PV) cells. These cells convert sunlight directly into electricity. When sunlight hits a PV cell, it excites electrons. This movement generates an electric current. The technology behind PV cells is fascinating yet complex. A simple understanding can help us appreciate its potential.
PV cells comprise various materials, often silicon. When sunlight penetrates, it frees electrons from atoms. This process creates a flow of electricity. However, the efficiency of PV cells varies. Factors like temperature and angle of sunlight matter greatly. In real-life applications, shadow from a tree or a building can drastically reduce output. It's essential to consider these details for effective solar setup.
**Tips:** When choosing solar panels, examine their efficiency ratings. Higher ratings often mean better performance. Also, always position your panels for maximum sun exposure. Regular maintenance is crucial, as dirt builds up can hinder performance. Reflecting on these simple actions can lead to significant energy savings.
Types of Solar Power Systems: Comparing Photovoltaic and Solar Thermal
Solar power systems come in two main types:
photovoltaic (PV) and
solar thermal.
PV systems convert sunlight directly into electricity using semiconductor materials like silicon.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), global PV capacity reached over
710 gigawatts (GW) in 2020, marking significant growth.
This technology is efficient and versatile,
often found on rooftops or in large solar farms. However, one challenge is the efficiency rate,
which averages around 15-20%.
Room for improvement exists.
On the other hand, solar thermal systems capture sunlight to produce heat. These systems use
collectors that heat a fluid, which can be used for water heating or even powering turbines.
Data from the Solar Heat Europe report indicates that solar thermal installations account for around
480 terawatt-hours (TWh) of heat annually in Europe alone.
Despite being reliable for heating applications, efficiency drops during cloudy weather.
This inconsistency can impact overall performance and reliability.
Ultimately, both systems provide valuable renewable energy options. They have distinct advantages and limitations.
PV excels in electricity generation,
while solar thermal shines in heating.
Choosing between them depends on specific energy needs and environmental conditions.
An informed decision requires understanding these nuances.
At times, a hybrid approach may serve as an optimal solution.
Global Impact of Solar Energy: Industry Growth and Renewable Capacity

The global impact of solar energy is profound. In recent years, the solar power industry has witnessed remarkable growth. According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), solar capacity doubled between 2017 and 2021. In 2021, global solar capacity reached over 1,000 gigawatts (GW). This surge reflects the increasing shift towards renewable energy sources.
As governments pursue cleaner energy goals, solar power plays a pivotal role. Countries worldwide are investing heavily. The Solar Energy Industries Association reported a 20% increase in solar jobs during 2020, showcasing the industry's potential for economic growth. Transitioning to solar could cut carbon emissions significantly. However, challenges remain. Energy storage technology must advance to fully harness solar power's potential.
Tips: Consider local solar incentives when exploring solar options. Research community solar programs, which let you share solar energy benefits without installing panels. It's a practical approach for many. Always consult experts before deciding on solar investments.
Key Advantages and Challenges of Adopting Solar Power Solutions
Solar power offers numerous advantages, making it an attractive energy solution. It is renewable and reduces dependence on fossil fuels. The International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA) reported that solar capacity grew by 22% globally in 2020. This growth points to a significant shift towards renewable energy.
Cost savings are also a key benefit. A report by Lazard showed that solar energy’s cost per megawatt-hour has dropped by 88% since 2009. This makes solar energy increasingly competitive with traditional electricity sources. Many households report a decrease in their energy bills after installing solar panels.
However, challenges remain. Initial installation costs can be high. Not everyone can afford upfront investments. Maintenance of solar panels can also bring unexpected costs over time. Furthermore, the efficiency of solar energy is weather-dependent. This can limit its reliability in some regions.
Tips: Consider local incentives for solar adoption. Research financing options, such as loans or leases. Evaluate your home’s solar potential with sunlight exposure analysis. Ensure you have a maintenance plan to keep your system running efficiently.
What is Solar Power and How Does It Work? - Key Advantages and Challenges of Adopting Solar Power Solutions
| Dimension | Description | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Sunlight converted to electricity | Solar panels |
| Efficiency Rate | Typical efficiency of solar panels | 15% - 22% |
| Installation Cost | Average cost per watt | $2.50 - $3.50 |
| Lifespan | Typical lifespan of solar panels | 25 - 30 years |
| Environmental Impact | Reduction in greenhouse gas emissions | ~90% reduction |
| Advantages | Renewable energy source & Low operating costs | Yes |
| Challenges | Intermittency & Initial costs | Yes |

